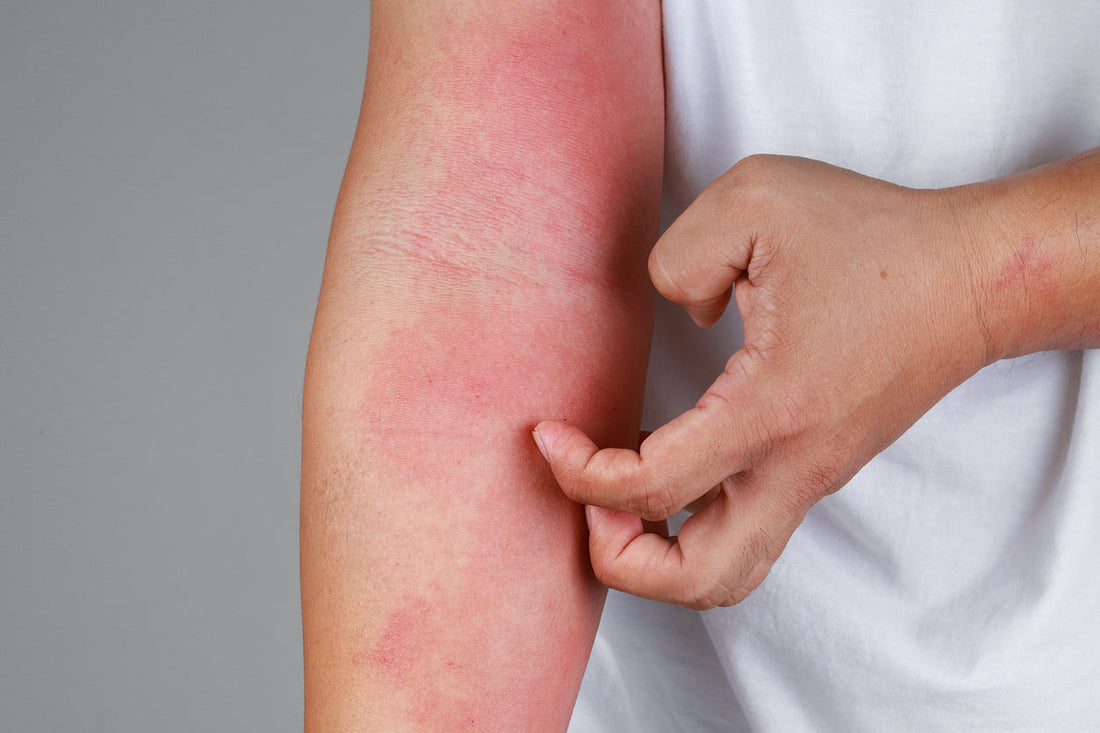
Seafood is a beloved culinary delight enjoyed by millions worldwide. However, for some, consuming seafood can pose serious health risks due to allergies. Understanding seafood allergies is crucial for those affected and their loved ones to ensure safety and enjoy peace of mind. This comprehensive guide will delve into the causes, symptoms, types, and management of seafood allergies, providing essential knowledge to navigate this common condition.
What Are Seafood Allergies?
A seafood allergy occurs when the immune system mistakenly identifies proteins in seafood as harmful substances, triggering an allergic reaction. This response can range from mild symptoms to severe, life-threatening reactions known as anaphylaxis. Seafood allergies are among the most common food allergies and can persist throughout a person’s life.
Types of Seafood Allergies
Seafood allergies are typically categorized into two main groups:
1. Shellfish Allergies
Shellfish allergies are more prevalent and involve two subcategories:
- Crustaceans: Includes shrimp, crab, and lobster. Crustacean allergies are the most common and are often severe.
- Mollusks: Includes clams, mussels, oysters, scallops, and squid. While mollusk allergies are less common, they can still cause significant reactions.
2. Fish Allergies
Fish allergies involve species such as salmon, tuna, cod, and halibut. Unlike shellfish allergies, fish allergies are often specific to certain types of fish, but cross-reactivity between different fish species can occur.
Common Symptoms of Seafood Allergies
Symptoms of seafood allergies can appear within minutes to a few hours after consumption. These symptoms vary in severity and may include:
- Mild Symptoms:
- Hives or skin rash
- Itchy or watery eyes
- Nasal congestion
- Stomach pain or nausea
- Severe Symptoms (Anaphylaxis):
- Difficulty breathing
- Swelling of the lips, tongue, or throat
- Rapid heartbeat
- Dizziness or fainting
Anaphylaxis requires immediate medical attention as it can be life-threatening. If you suspect someone is experiencing anaphylaxis, administer an epinephrine injection if available and call emergency services.
Diagnosing Seafood Allergies
If you suspect a seafood allergy, consult an allergist for a proper diagnosis. The diagnostic process may include:
- Medical History: The allergist will review your symptoms and family history of allergies.
- Skin Prick Test: A small amount of seafood protein is applied to the skin, and the area is monitored for a reaction.
- Blood Test: Measures specific antibodies (IgE) associated with allergic reactions.
- Oral Food Challenge: Performed under medical supervision, this test involves consuming small amounts of the suspected allergen to monitor for a reaction.
Managing Seafood Allergies
While there is no cure for seafood allergies, effective management can prevent reactions and ensure safety. Here’s how:
1. Avoidance
The most crucial step in managing seafood allergies is avoiding the allergen entirely. This includes:
- Reading Labels: Always check ingredient lists for hidden seafood components, such as fish sauce or shellfish extracts.
- Dining Out: Inform restaurant staff of your allergy and ask about potential cross-contact in food preparation.
- Cross-Contact Precautions: Use separate utensils, cutting boards, and cookware to prevent cross-contact with seafood.
2. Emergency Preparedness
Being prepared for accidental exposure is vital:
- Epinephrine Auto-Injector: Always carry an epinephrine auto-injector, such as an EpiPen, and know how to use it.
- Allergy Action Plan: Work with your allergist to develop a plan outlining steps to take in case of a reaction.
- Medical Identification: Wear a medical alert bracelet or carry a card indicating your allergy.
3. Education and Support
Educate yourself and others about your allergy:
- Family and Friends: Teach them about your allergy and how to recognize symptoms.
- Schools and Workplaces: Ensure staff are aware of your allergy and know how to respond in an emergency.
- Support Groups: Join online or local support groups to connect with others managing seafood allergies.
Cross-Reactivity and Seafood Allergies
Cross-reactivity occurs when the immune system reacts to proteins in similar allergens. For instance, individuals allergic to shrimp may also react to crab or lobster. Understanding cross-reactivity is essential for avoiding unexpected reactions.
Living with Seafood Allergies: Practical Tips
- Shop Smart: Choose allergen-free brands and shop at stores with clear labeling policies.
- Travel Safely: Learn how to communicate your allergy in different languages and research local cuisine before traveling.
- Substitute Ingredients: Use seafood substitutes like plant-based fish alternatives or tofu in recipes.
- Stay Informed: Keep up with allergy research and advancements in treatments.
The Future of Seafood Allergy Management
Research into food allergies is ongoing, offering hope for new treatments. Potential advancements include:
- Oral Immunotherapy: Gradually exposing individuals to small amounts of the allergen to build tolerance.
- Biological Therapies: Targeting specific immune responses to reduce allergy severity.
- Improved Diagnostics: Developing more accurate and less invasive diagnostic methods.
Managing a seafood allergy may seem daunting, but with the right knowledge and precautions, it’s entirely possible to lead a safe and fulfilling life. By understanding the nature of seafood allergies, recognizing symptoms, and taking proactive measures, you can navigate the culinary world with confidence. Remember, preparation and education are your best allies in living well with seafood allergies.